Ultrasound machines have become indispensable tools in the medical field, providing doctors and healthcare professionals with the ability to diagnose and monitor various conditions without the need for invasive procedures. In Canada, where healthcare technology is embraced and highly valued, understanding how these machines work is crucial for both medical professionals and the public. This article dives into the mechanics of ultrasound machines, their applications, and the regulatory environment in Canada that ensures their safe and effective use.
The Basics of Ultrasound Technology
At its core, ultrasound technology utilizes sound waves to produce images of the inside of the body. Unlike X-rays, which use ionizing radiation, ultrasound involves the transmission and reception of high-frequency sound waves, which are beyond the range of human hearing. When these sound waves are directed into the body, they bounce off tissues, organs, and other structures at different rates, depending on the density of the materials they encounter.
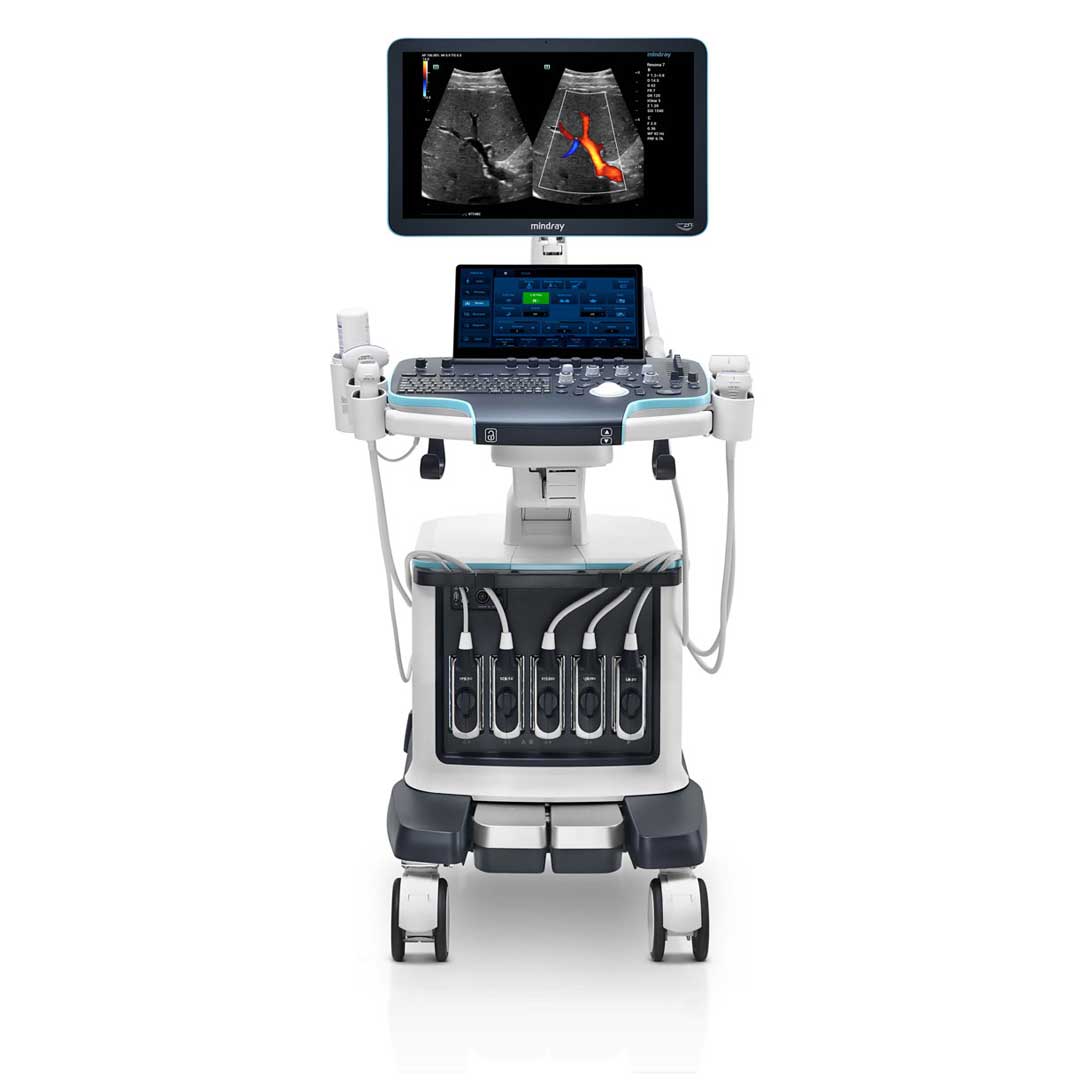
The ultrasound machine consists of several key components:
- Transducer probe: This device emits the sound waves into the body and receives the echoes that bounce back.
- Central processing unit (CPU): The CPU analyzes the received echoes and converts them into visual images.
- Display: The processed images are displayed on a screen, providing real-time, dynamic views of the internal workings of the body.
- Control panel: This allows the operator to adjust settings and control the scanning process.
The process of converting sound waves into visual images is known as sonography or ultrasonography. The transducer probe plays a critical role in this process. It contains piezoelectric crystals that vibrate when an electric current is applied, producing sound waves. When these waves hit an interface between different types of tissues, some of the waves are reflected back to the probe and are subsequently converted into electrical signals. The CPU then interprets these signals to create images.
Applications of Ultrasound in Canada
In Canada, ultrasound technology is widely used across various medical specialties, including:
- Obstetrics and gynecology: For monitoring fetal development and diagnosing conditions related to the female reproductive system.
- Cardiology: To assess the heart’s structure and function, including valve operations and blood flow.
- Radiology: For examining soft tissues, muscles, blood vessels, and organs like the liver, kidneys, and pancreas.
- Musculoskeletal: To assess injuries to muscles, tendons, and joints.
The versatility of ultrasound makes it a preferred diagnostic tool, particularly because it is non-invasive, has no known side effects, and provides real-time images.
Impact of Ultrasound on Patient Education and Engagement
 The advent of ultrasound technology has significantly impacted patient education and engagement, offering a unique window into one’s health that was previously unavailable. This section will discuss how ultrasound imaging has become a tool for enhancing patient understanding and involvement in their healthcare journey. In Canada, the accessibility of ultrasound technology allows patients to see real-time images of their condition, fostering a deeper connection and comprehension of their medical issues. Furthermore, it examines how healthcare providers use these images to educate patients about their diagnoses, treatment options, and the importance of monitoring, thereby empowering patients to take an active role in their healthcare.
The advent of ultrasound technology has significantly impacted patient education and engagement, offering a unique window into one’s health that was previously unavailable. This section will discuss how ultrasound imaging has become a tool for enhancing patient understanding and involvement in their healthcare journey. In Canada, the accessibility of ultrasound technology allows patients to see real-time images of their condition, fostering a deeper connection and comprehension of their medical issues. Furthermore, it examines how healthcare providers use these images to educate patients about their diagnoses, treatment options, and the importance of monitoring, thereby empowering patients to take an active role in their healthcare.
Economic Implications of Ultrasound Technology in the Canadian Healthcare System
Ultrasound technology not only offers clinical benefits but also presents economic considerations within the healthcare system. This section will explore the cost-effectiveness of ultrasound imaging compared to other diagnostic methods, its impact on reducing the need for more invasive and expensive procedures, and the overall economic implications for the Canadian healthcare system. It will also delve into funding models, reimbursement policies, and the potential for ultrasound technology to contribute to more sustainable healthcare by alleviating system pressures and optimizing resource allocation.
Ethical Considerations Surrounding Advanced Prenatal Ultrasound Technologies
Advanced prenatal ultrasound technologies, such as 3D and 4D imaging, have revolutionized prenatal care, offering detailed visuals of the fetus during pregnancy. While these advancements provide critical information for the management of pregnancy, they also raise ethical considerations. This section will address the ethical dilemmas posed by advanced prenatal ultrasounds, including concerns over non-medical uses, potential for increased anxiety among expectant parents, and the implications of early detection of fetal abnormalities. It will examine how these issues are navigated within the Canadian healthcare context, focusing on guidelines for the responsible use of these technologies, informed consent, and the role of healthcare professionals in providing support and counseling to expectant parents.
The Regulatory Environment in Canada
Health Canada plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of ultrasound machines used across the country. All medical devices, including ultrasound machines, must undergo a rigorous approval process before they can be marketed in Canada. This process involves the assessment of the device’s safety, effectiveness, and quality, ensuring that it meets the standards set by the Medical Devices Regulations under the Food and Drugs Act.
Manufacturers and healthcare facilities must also adhere to standards and guidelines set by Canadian and international organizations, such as the Canadian Standards Association (CSA) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). These standards cover various aspects of ultrasound equipment, including electrical safety, acoustic output, and the qualification of operators.
Training and Education for Ultrasound Technicians in Canada
 The effectiveness of ultrasound technology not only depends on the quality of the machines but also on the skill and expertise of the operators. In Canada, ultrasound technicians, also known as diagnostic medical sonographers, undergo specialized training through accredited programs. These programs cover anatomy, physiology, patient care, physics, and hands-on training with ultrasound equipment.
The effectiveness of ultrasound technology not only depends on the quality of the machines but also on the skill and expertise of the operators. In Canada, ultrasound technicians, also known as diagnostic medical sonographers, undergo specialized training through accredited programs. These programs cover anatomy, physiology, patient care, physics, and hands-on training with ultrasound equipment.
Certification is typically required by employers and is offered through organizations such as the Canadian Association of Registered Diagnostic Ultrasound Professionals (CARDUP) and the Sonography Canada. Continuing education is also emphasized in the profession to keep pace with advancements in technology and techniques.
Technical Advancements in Ultrasound Technology
Recent years have seen significant advancements in ultrasound technology, enhancing its application and efficacy in diagnostic medicine. Innovations such as high-definition imaging, elastography (which assesses the elasticity of soft tissue), and contrast-enhanced ultrasound (using microbubble contrast agents to improve image clarity) have broadened the scope of ultrasound diagnostics. Canadian healthcare has been at the forefront of adopting these technologies, offering patients access to state-of-the-art diagnostic tools. This section explores these advancements and their implications for patient care in Canada.
Integration of Ultrasound in Canadian Healthcare Education
The integration of ultrasound technology into Canadian healthcare education has been pivotal in ensuring the efficient and effective use of this diagnostic tool. Medical schools across Canada have begun to incorporate ultrasound training into their curricula, providing future physicians with the skills and knowledge to utilize ultrasound in their practice. Moreover, specialized ultrasound technician programs have evolved to meet the high standards of proficiency required in the field. This section will discuss the educational pathways available for aspiring ultrasound technicians and physicians in Canada, highlighting the importance of education in advancing ultrasound diagnostics.
Patient Experiences with Ultrasound in Canada
Patient experiences are a crucial aspect of understanding the impact of ultrasound technology in healthcare. This section will explore testimonials and case studies from Canadian patients who have undergone ultrasound procedures. It will examine the role of ultrasound in patient diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring, shedding light on the technology’s benefits from a patient’s perspective, including its non-invasiveness, safety, and ability to provide immediate results.
Ethical Considerations in Ultrasound Imaging
As with all medical technologies, the use of ultrasound comes with its set of ethical considerations. Issues such as the privacy of ultrasound images, informed consent, and the implications of early diagnosis (such as in prenatal screenings) are of particular concern. This section will delve into the ethical landscape surrounding ultrasound use in Canada, discussing how healthcare providers navigate these issues to ensure patient rights and dignity are upheld.
Ultrasound vs. Other Imaging Technologies
While ultrasound is a critical tool in diagnostic imaging, it is one of several technologies available to healthcare providers, including X-rays, CT scans, and MRI. Each technology has its unique advantages and limitations. This section will compare ultrasound with these other imaging modalities, considering factors such as imaging capabilities, cost, safety, and availability. The comparison will provide insight into how Canadian healthcare professionals choose the most appropriate imaging technique for different medical conditions.
The Role of Public and Private Healthcare in Ultrasound Services
Canada’s healthcare system is characterized by its public foundation, but private healthcare services also play a role, particularly in diagnostic imaging. This section will explore how ultrasound services are provided within Canada’s mixed healthcare system, examining the balance between public and private offerings, funding mechanisms, and accessibility issues. It will also discuss how this system impacts the availability of ultrasound technology across different regions, particularly in rural versus urban settings.
Environmental Impact of Ultrasound Devices
The environmental footprint of medical devices, including ultrasound machines, is an increasingly important consideration. This section will explore the lifecycle of ultrasound equipment, from manufacturing and clinical use to disposal or recycling. It will discuss the initiatives within Canada to reduce the environmental impact of these devices, such as energy-efficient models, programs for recycling old machines, and research into more sustainable materials and manufacturing processes. The goal is to understand how the healthcare sector is addressing environmental sustainability while maintaining high standards of patient care.
Collaboration Between Canadian Universities and Healthcare Industry
Canadian universities play a crucial role in advancing ultrasound technology through research and development. This section will highlight successful collaborations between academic institutions and the healthcare industry, focusing on innovations in ultrasound imaging, therapeutic applications, and training methods. Examples include the development of portable ultrasound devices, advancements in ultrasound-guided procedures, and the integration of artificial intelligence to improve diagnostic accuracy. These collaborations not only drive technological innovation but also ensure that Canadian healthcare providers have access to cutting-edge ultrasound solutions.
International Partnerships in Ultrasound Technology
Canada’s involvement in international partnerships and projects related to ultrasound technology underscores its commitment to global health and innovation. This section will discuss Canada’s role in collaborative efforts to improve ultrasound accessibility and training in developing countries, contributions to global research initiatives, and partnerships with international organizations and other countries. These activities not only enhance the global profile of Canadian healthcare innovation but also contribute to the worldwide advancement of medical ultrasound technology.
The Future of Ultrasound Technology in Telehealth
The integration of ultrasound technology into telehealth represents a promising frontier for expanding access to diagnostic services, particularly in remote and underserved communities. This section will examine how portable and handheld ultrasound devices are being used in telehealth applications, allowing healthcare professionals to conduct remote diagnostics with the support of real-time data transmission and consultation. It will explore current projects and pilot programs in Canada that utilize ultrasound in telehealth, highlighting the challenges, successes, and potential for future expansion.
Future of Ultrasound Technology in Canada
The future of ultrasound technology in Canada looks promising, with ongoing advancements aimed at improving image quality, reducing costs, and expanding applications. Innovations such as 3D and 4D ultrasounds, which provide more detailed and dynamic images, are already being used in some Canadian healthcare facilities. There is also a growing interest in portable and handheld ultrasound devices, which can make diagnostic imaging more accessible, especially in remote and underserved areas.
In addition, research and development efforts are focused on enhancing the capabilities of ultrasound through artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies have the potential to automate aspects of the imaging process, improve diagnostic accuracy, and personalize patient care.