Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Is Ultrasound?
- Top Clinical Benefits of Ultrasound
- Benefits of Ultrasound in Diagnostic Imaging
- Technological Advancements Enhancing Ultrasound
- Benefits of Portable and Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS)
- Cost and Safety Advantages
- Applications Across Medical Specialties
- Manufacturing Innovations in Ultrasound Technology
- Regulatory Considerations and Global Adoption
- Key Takeaways
- FAQs
Introduction
Ultrasound technology has undergone remarkable evolution since its initial medical use in the 1940s. Today, it is an indispensable tool in modern medicine, used for everything from prenatal imaging to guided biopsies and therapeutic interventions. With rising demand for non-invasive, real-time diagnostics, ultrasound’s value in healthcare continues to grow.
This article explores the benefits of ultrasound from a multifaceted perspective—clinical, technological, economic, and manufacturing—highlighting why this modality remains a cornerstone in diagnostics and patient care.
What Is Ultrasound?
Ultrasound, or ultrasonography, is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to visualize internal body structures. Unlike radiographic methods, ultrasound does not involve ionizing radiation, making it a safer option for both patients and healthcare providers.
Key components of an ultrasound system:
- Transducer (probe) – emits and receives sound waves
- Processing unit – interprets signals and creates images
- Display monitor – shows real-time anatomical images
- Software – enables measurements, annotations, and archiving
Top Clinical Benefits of Ultrasound
1. Non-Invasive and Painless
Ultrasound does not require incisions, injections, or exposure to radiation. This makes it ideal for routine monitoring, preventive screenings, and sensitive populations (e.g., pregnant women, children).
2. Real-Time Imaging
Ultrasound allows physicians to observe organ motion and blood flow in real time. This is crucial for:
- Cardiovascular assessments (e.g., echocardiography)
- Fetal monitoring
- Interventional procedures like biopsies and fluid drainage
3. High Diagnostic Accuracy
In skilled hands, ultrasound delivers high specificity and sensitivity, especially in soft tissue evaluations. Doppler ultrasound enhances the ability to visualize blood vessels and flow abnormalities.
4. Accessibility and Speed
Ultrasound machines can be deployed quickly in a variety of settings—from outpatient clinics to battlefields—allowing immediate clinical decisions.
Benefits of Ultrasound in Diagnostic Imaging
Ultrasound has revolutionized diagnostic imaging across multiple domains:
| Diagnostic Area | Benefits of Ultrasound |
| Obstetrics | Safe monitoring of fetal development |
| Cardiology | Non-invasive heart assessments (e.g., valve function, ejection fraction) |
| Abdominal | Real-time liver, kidney, gallbladder scans |
| Musculoskeletal | Joint, tendon, and ligament visualization |
| Thyroid and Breast | Accurate nodule characterization without radiation |
Ultrasound also complements CT and MRI by providing dynamic assessment, such as compressibility in DVT evaluations or motion tracking in musculoskeletal exams.
Technological Advancements Enhancing Ultrasound
1. 3D/4D Imaging
- Enables real-time volumetric imaging
- Widely used in fetal diagnostics and tumor localization
2. Elastography
- Measures tissue stiffness
- Useful for detecting liver fibrosis, tumors, and thyroid lesions
3. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS)
- Improves visualization of vascular structures
- Provides detailed perfusion imaging without radiation
4. AI Integration
- AI algorithms assist with image acquisition, anomaly detection, and reporting
- Reduces operator dependency and increases diagnostic confidence
5. Wireless and Handheld Devices
- Allow bedside assessments and telemedicine integration
- Power decentralized healthcare in rural and low-resource settings
Benefits of Portable and Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS)
The emergence of POCUS has transformed how clinicians diagnose and treat patients:
- Rapid assessments at the bedside during trauma or cardiac arrest
- Streamlined workflows in emergency rooms and ICUs
- Reduces need for costly CT scans or unnecessary referrals
- Improves outcomes through faster intervention
Clinical Example:
POCUS is now standard in many medical schools and residency programs. A study published in The Journal of Emergency Medicine found that incorporating ultrasound into initial trauma evaluation reduced diagnostic errors by 20%.
Cost and Safety Advantages
Safety Benefits
- No radiation: ideal for pregnancy, pediatrics, and repeat imaging
- No contrast allergies: contrast agents used in CEUS are better tolerated
- Lower infection risk than invasive procedures
Economic Benefits
| Factor | Ultrasound | CT Scan | MRI |
| Average cost | $100–$1,000 | $500–$3,000 | $1,000–$5,000 |
| Setup cost | Low | Moderate | High |
| Operational costs | Minimal | High | High |
| Turnaround time | Minutes | 30+ mins | 45+ mins |
Ultrasound offers the best cost-benefit ratio for many diagnostic and interventional procedures, particularly in primary care and low-income settings.
Applications Across Medical Specialties
1. Emergency Medicine
- FAST exam (Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma)
- Cardiac arrest and pericardial effusion detection
2. Obstetrics & Gynecology
- Fetal anomaly screening
- Ovulation monitoring and intrauterine device placement
3. Cardiology
- Echocardiograms for valvular disease, CHF, congenital heart conditions
4. Urology
- Prostate imaging
- Bladder volume assessments
5. Oncology
- Tumor localization
- Guided biopsies and ablation therapies
6. Anesthesiology
- Regional nerve blocks
- Vascular access under ultrasound guidance
Manufacturing Innovations in Ultrasound Technology
The manufacturing landscape of ultrasound systems is undergoing rapid change, driven by:
1. Miniaturization of Components
- MEMS-based transducers enable handheld designs
- Improved thermal control and image resolution
2. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
- Custom probes for specialized procedures
- Rapid prototyping of ergonomic housings
3. Sustainable Design
- Biodegradable materials for single-use transducers
- Energy-efficient systems for green healthcare
4. Modular System Architectures
- Enables upgradeable software/hardware
- Supports personalized configurations for different specialties
5. Automated Quality Testing
- In-line testing for transducer calibration
- AI-driven error detection in manufacturing lines
Manufacturers like GE HealthCare, Philips, and Butterfly Network are leading the charge with cloud-based ultrasound platforms and AI-enhanced diagnostic tools.
Regulatory Considerations and Global Adoption
Ultrasound systems must comply with regulatory standards that ensure safety and efficacy:
Key Regulatory Bodies:
- FDA (U.S.) – 510(k) clearance for Class II devices
- Health Canada – Class II/III device licensing
- CE Mark (Europe) – MDD/MDR compliance
Global Trends:
- WHO-endorsed as an essential diagnostic tool for LMICs
- Tele-ultrasound growing in global health and rural outreach
- Increasing inclusion in value-based care reimbursement models
Regulatory Challenge:
With the rise of AI in ultrasound, there’s an increasing push for regulatory frameworks that address software-as-a-medical-device (SaMD) oversight, particularly regarding AI transparency and validation.
Expanding Clinical Applications of Ultrasound: Beyond Imaging
While ultrasound is widely recognized for its diagnostic capabilities, it is increasingly being leveraged for interventional and therapeutic procedures. These expanded applications underscore its growing role not just in “seeing” but in treating disease.
Ultrasound-Guided Interventions
Ultrasound guidance has become the gold standard in numerous minimally invasive procedures due to its ability to enhance precision, reduce complication rates, and minimize patient discomfort.
Common Ultrasound-Guided Procedures:
- Central and peripheral line placements
- Thoracentesis and paracentesis
- Biopsies (thyroid, liver, breast, lymph nodes)
- Abscess drainage
- Joint and nerve injections
- Tumor ablation therapy
Compared to landmark-based techniques, ultrasound guidance reduces the risk of vascular puncture, organ damage, and procedural failure. In a study published by BMJ Open, ultrasound-guided central line insertion reduced complication rates by 57% compared to blind methods.
Therapeutic Ultrasound
Therapeutic ultrasound uses focused sound energy to alter tissues for clinical benefit. It is increasingly employed in:
1. High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU)
Used to thermally ablate tumors in:
- Prostate cancer
- Liver cancer
- Uterine fibroids
HIFU is non-invasive, reduces hospital stays, and avoids the systemic effects of chemotherapy or radiation.
2. Ultrasound Physiotherapy
Low-intensity ultrasound is used to promote:
- Soft tissue healing
- Bone fracture repair
- Pain relief in musculoskeletal injuries
3. Lithotripsy
Ultrasound waves fragment kidney or gallstones for easier passage, avoiding surgical removal.
These therapeutic uses are being integrated into more mainstream treatment pathways, particularly in oncology and pain management.
Ultrasound in Global Health: Bridging Diagnostic Gaps
Ultrasound’s portability, affordability, and safety make it uniquely suited for resource-limited settings where access to CT or MRI is often non-existent.
The Challenge:
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 4.7 billion people lack access to basic diagnostic imaging. Rural clinics and developing nations often suffer from a lack of imaging infrastructure and trained personnel.
The Solution:
- Portable, battery-powered ultrasounds that connect to tablets or smartphones
- Tele-ultrasound systems allowing remote interpretation by specialists
- POCUS training programs enabling frontline health workers to perform essential scans
Example Initiative:
The RAD-AID Ultrasound Program provides equipment and training to underserved regions across Africa, Asia, and Latin America. In one pilot in Rwanda, access to prenatal ultrasound reduced maternal mortality risk by 35% through early detection of high-risk pregnancies.
The Role of Ultrasound in Value-Based and Preventive Care
Healthcare systems worldwide are shifting toward value-based care models, emphasizing prevention, early detection, and cost efficiency. Ultrasound aligns perfectly with this approach due to:
1. Early Disease Detection
Ultrasound identifies abnormalities before symptoms arise, such as:
- Aortic aneurysms in men over 65
- Liver fibrosis in hepatitis patients
- Thyroid nodules and early-stage cancers
2. Ongoing Monitoring
Regular, safe follow-ups can be done without repeated radiation exposure. Common uses include:
- Chronic kidney disease progression
- Tumor response to therapy
- Congenital anomaly surveillance
3. Triage and Decision Support
In primary care and emergency settings, ultrasound helps prioritize care, reducing unnecessary imaging and hospital admissions.
Impact on Health Economics:
A 2023 study in Health Affairs showed that integrating POCUS into family medicine reduced downstream imaging costs by $2,400 per 100 patients without compromising diagnostic accuracy.
Workforce Development and Ultrasound Training
As the use of ultrasound expands, so too does the need for comprehensive training programs that ensure consistent image quality and interpretation accuracy.
Training Pathways:
- Formal certification programs (e.g., American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography)
- Short-term POCUS fellowships
- Online simulations and AI-guided learning modules
- Medical school integration – Ultrasound now introduced in over 70% of North American med school curricula
AI-Enhanced Training:
AI-powered platforms now provide real-time scanning feedback, guiding probe positioning and identifying key anatomical landmarks. These systems can:
- Standardize technique among providers
- Accelerate skill acquisition
- Reduce cognitive load during exams
Example Platform:
Butterfly Academy, integrated with Butterfly iQ devices, uses gamification and visual cues to teach scanning techniques in remote areas, closing training gaps in less than 12 weeks.
Integration Into the Digital Health Ecosystem
Ultrasound’s future lies not just in hardware but in its integration into broader digital health ecosystems. Cloud connectivity and data interoperability are enabling:
- Seamless integration with Electronic Medical Records (EMRs)
- Real-time remote collaboration through tele-ultrasound
- Longitudinal patient tracking via AI-assisted scan comparisons
Example:
GE’s Vscan Air integrates with cloud-based health platforms to allow image sharing, AI diagnostics, and remote consultation, facilitating continuity of care in home health and post-acute settings.
This convergence supports the quadruple aim in healthcare: better outcomes, lower costs, improved patient experience, and enhanced provider satisfaction.
Ultrasound’s Role in Pandemic Preparedness and Crisis Response
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the value of ultrasound as a frontline imaging modality. Portable devices were rapidly deployed for:
- Lung ultrasound to assess viral pneumonia severity
- Cardiac evaluation in ICU patients with myocarditis or thromboembolic complications
- Vascular access and DVT detection under PPE constraints
Key benefits during the pandemic:
- Avoided moving critically ill patients to radiology departments
- Enabled rapid triage and escalation decisions
- Limited contamination and equipment exposure
Ultrasound’s agility and infection-control profile make it an essential asset in pandemic preparedness toolkits and disaster response strategies globally.
Key Takeaways
- Ultrasound offers real-time, radiation-free diagnostics suitable for diverse clinical settings
- Portability and low cost make it ideal for both high-tech hospitals and remote clinics
- Technological advances such as AI, elastography, and CEUS are expanding its diagnostic range
- Manufacturing innovations are driving device miniaturization, automation, and sustainability
- A growing role in emergency medicine, primary care, and global health underscores its future potential
FAQs on the Benefits of Ultrasound
Is ultrasound safe for repeated use?
Yes. Ultrasound uses non-ionizing sound waves, making it safe for repeated imaging—especially during pregnancy or chronic condition monitoring.
Can ultrasound detect cancer?
It can. While not always definitive, ultrasound helps identify tumors, guide biopsies, and monitor treatment response. It’s particularly useful for breast, liver, thyroid, and prostate cancer.
How does ultrasound compare to MRI or CT?
Ultrasound is faster, cheaper, and safer (no radiation), though it may lack the resolution of MRI or CT for deep tissue or bone structures.
Who can perform ultrasounds?
Traditionally sonographers or radiologists, but with POCUS training, many physicians—including ER doctors, anesthesiologists, and OB/GYNs—routinely use it.
Are AI-powered ultrasounds available now?
Yes. AI is already integrated in many modern systems, assisting with diagnostics, measurements, and workflow optimization. Regulatory frameworks for these systems are evolving.
Reinforcing the Value Proposition of Ultrasound
Ultrasound is no longer a niche imaging modality—it is a frontline diagnostic and therapeutic technology. Its broad utility across specialties, combined with rapid technological evolution, positions it as a key driver in the shift toward personalized, preventive, and portable medicine.
From guiding lifesaving procedures in emergency settings to empowering community health workers in remote villages, ultrasound is transforming the delivery, accessibility, and quality of healthcare worldwide.
As we look ahead, continued investment in AI integration, training infrastructure, and equitable access will be crucial to fully realize ultrasound’s potential as a democratizing force in global health.
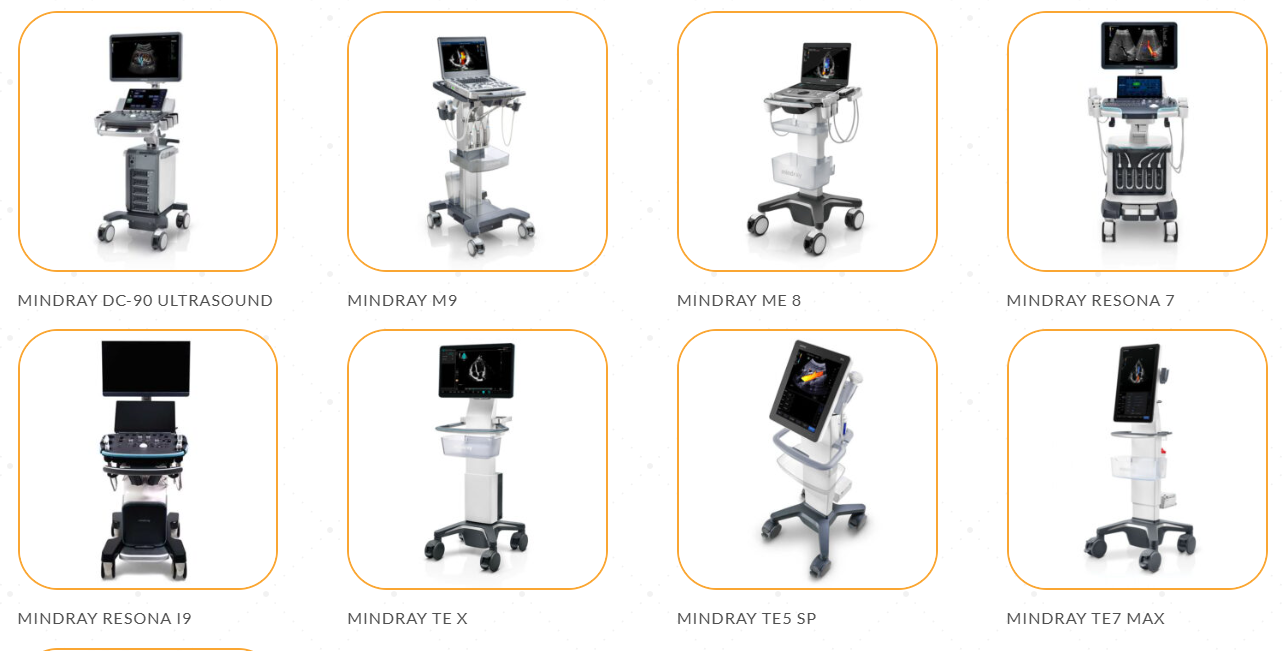
Highlighted Mindray point-of-care ultrasound machine models available through BOMImed include Mindray TE Air Ultrasound, Mindray M9, Mindray ME 8, Mindray TE X, Mindray TE5 SP, Mindray TE7 Max, Mindray Z.One Pro. Discover the difference with BOMImed’s comprehensive range of portable ultrasound machines, designed to enhance diagnostic efficiency and patient care.
Shop by category: Point of Care Ultrasound – Portable Ultrasound – Radiology Ultrasound