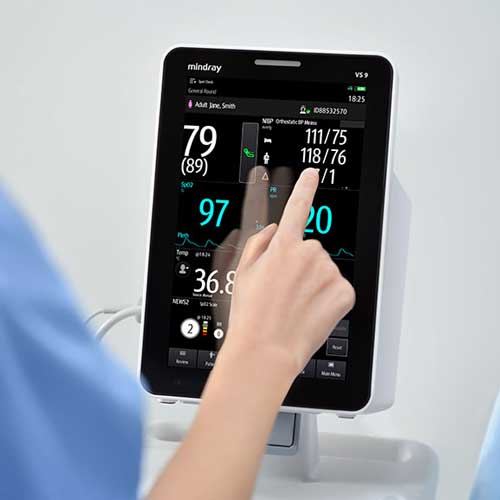
Patient monitoring has become a cornerstone of medical practices, allowing healthcare providers to continuously track the physiological functions of patients. Canada, known for its robust healthcare system, has been at the forefront of integrating advanced patient monitoring technologies to enhance patient care and outcomes. This article delves into the evolution of patient monitoring in Canada, its current state, the challenges faced, and the promising future it holds.
Historical Overview
The concept of patient monitoring is not new; it has been an integral part of healthcare for centuries, evolving from simple observational practices to sophisticated technological systems. In Canada, the journey began with basic tools like the stethoscope and blood pressure cuffs, gradually advancing to incorporate electronic monitoring devices in the mid-20th century. These developments marked a significant shift towards more accurate and real-time tracking of patient health.
The Current Landscape of Patient Monitoring in Canada
Today, patient monitoring in Canada encompasses a wide array of technologies, from wearable devices and bedside monitors to remote patient monitoring (RPM) systems. These technologies enable the continuous observation of vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and more, facilitating timely medical interventions.
Technological Advancements
Canada has embraced technological advancements to enhance patient monitoring. Wearable technologies, for example, allow for the monitoring of patients in real-time, providing data directly to healthcare professionals. This data-driven approach enables personalized care plans and interventions, improving patient outcomes.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
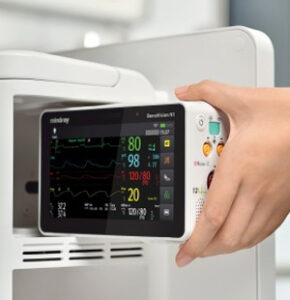 RPM has gained significant traction in Canada, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. This approach allows patients to be monitored outside of traditional healthcare settings, reducing the strain on healthcare facilities and enabling patients to receive care in the comfort of their homes. RPM has shown particular promise in managing chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and respiratory conditions.
RPM has gained significant traction in Canada, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. This approach allows patients to be monitored outside of traditional healthcare settings, reducing the strain on healthcare facilities and enabling patients to receive care in the comfort of their homes. RPM has shown particular promise in managing chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and respiratory conditions.
Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
The integration of patient monitoring systems with EHRs in Canada has streamlined the process of data collection and analysis. This integration allows healthcare providers to access comprehensive patient data, facilitating informed decision-making and enhancing the continuity of care.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite the progress, the implementation of advanced patient monitoring systems in Canada faces several challenges. These include issues related to privacy and security, the digital divide, and the need for standardization.
Privacy and Security Concerns
With the increasing use of digital technologies, concerns regarding patient data privacy and security have emerged. To address these concerns, Canada has implemented stringent regulations, such as the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA), to safeguard patient information.
Bridging the Digital Divide
The digital divide, referring to the gap between those with access to digital technologies and those without, poses a significant challenge to the widespread adoption of RPM. To mitigate this, the Canadian government and healthcare providers are working to ensure broader access to technology and internet services, especially in rural and remote areas.
Standardization and Interoperability
The lack of standardization and interoperability among patient monitoring systems can hinder their effectiveness. Canada is making strides towards establishing uniform standards and protocols to ensure seamless communication between different technologies and healthcare systems.
Patient and Provider Perspectives on Monitoring Technologies
 Understanding the perspectives of both patients and healthcare providers is crucial for the successful adoption of patient monitoring technologies. Patients seek convenience, reassurance, and empowerment in managing their health, while providers look for reliability, accuracy, and ease of integration with existing workflows. Surveys and studies indicate a generally positive outlook from both groups, with patients appreciating the increased autonomy and providers valuing the enhanced ability to make informed clinical decisions. However, concerns about over-reliance on technology, potential loss of personal interaction, and the need for training highlight areas for improvement.
Understanding the perspectives of both patients and healthcare providers is crucial for the successful adoption of patient monitoring technologies. Patients seek convenience, reassurance, and empowerment in managing their health, while providers look for reliability, accuracy, and ease of integration with existing workflows. Surveys and studies indicate a generally positive outlook from both groups, with patients appreciating the increased autonomy and providers valuing the enhanced ability to make informed clinical decisions. However, concerns about over-reliance on technology, potential loss of personal interaction, and the need for training highlight areas for improvement.
Public-Private Partnerships in Advancing Patient Monitoring
The development and implementation of advanced patient monitoring systems often require resources and expertise beyond what public healthcare institutions can provide alone. Public-private partnerships (PPPs) have emerged as a powerful mechanism to drive innovation in this space. Through collaboration, these partnerships leverage the strengths of both sectors—public sector’s focus on patient care and equity, and the private sector’s drive for innovation and efficiency. PPPs in Canada have facilitated the development of cutting-edge technologies, the establishment of telehealth services, and the creation of scalable models for remote patient monitoring.
Advancements in Data Analytics and Interoperability
The effectiveness of patient monitoring systems heavily relies on the ability to analyze large volumes of data and share information seamlessly across different healthcare platforms. Advances in data analytics, including predictive modeling and machine learning, have greatly enhanced the ability to interpret complex health data. Interoperability—the capacity for different systems and software to exchange and make use of information—remains a challenge, yet progress is being made through the adoption of standardized data formats and protocols. Canada’s commitment to improving interoperability is evident in its support for national and international standards, facilitating better patient care coordination and outcomes.
Environmental Impact of Healthcare Technologies
As patient monitoring technologies proliferate, their environmental impact becomes an increasingly important consideration. The production, use, and disposal of electronic devices and batteries raise concerns about resource consumption and electronic waste. In response, Canadian healthcare organizations and technology companies are exploring sustainable practices, such as recycling programs, energy-efficient devices, and the development of greener technologies. Balancing the environmental footprint with the benefits of patient monitoring technologies is essential for sustainable healthcare.
Personalized Medicine Through Patient Monitoring
The vast amounts of data generated by patient monitoring technologies hold the promise for personalized medicine, tailoring healthcare interventions to individual patient needs and genetic profiles. In Canada, initiatives in genomics and biotechnology are converging with patient monitoring advancements to create more targeted and effective treatments. This approach not only improves patient outcomes but also enhances the efficiency of the healthcare system by focusing resources on the most effective interventions for each patient.
The Future of Patient Monitoring in Canada
The future of patient monitoring in Canada is bright, with several promising trends and innovations on the horizon.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into patient monitoring systems is set to revolutionize healthcare. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and recommend interventions, leading to more proactive and personalized patient care.
Wearable Technology and Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
The advancement of wearable technology and the emergence of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) are expected to further enhance patient monitoring. These technologies will enable even more precise and real-time tracking of health metrics, improving the ability to manage and prevent health issues.
Telehealth Expansion
Telehealth has seen exponential growth, and its integration with patient monitoring systems is anticipated to continue. This will allow healthcare providers to offer comprehensive care remotely, making healthcare more accessible and efficient.
Patient Empowerment
The future of patient monitoring also lies in empowering patients to take an active role in their healthcare. Technologies that provide patients with access to their own health data and insights can facilitate better health literacy and engagement in their care.
Innovative Models of Care Enabled by Patient Monitoring
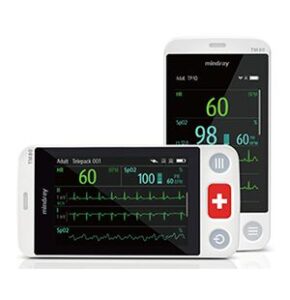 The advent of sophisticated patient monitoring technologies has paved the way for innovative models of care that prioritize patient-centric approaches, efficiency, and effectiveness. One such model is the concept of virtual wards or hospitals at home. These models leverage RPM technologies to provide hospital-level care to patients in their homes, reducing the need for hospital admissions and allowing healthcare systems to allocate resources more efficiently. Another innovative model is predictive healthcare, which utilizes AI and ML algorithms to analyze monitoring data and predict acute medical events before they occur, potentially saving lives and reducing healthcare costs.
The advent of sophisticated patient monitoring technologies has paved the way for innovative models of care that prioritize patient-centric approaches, efficiency, and effectiveness. One such model is the concept of virtual wards or hospitals at home. These models leverage RPM technologies to provide hospital-level care to patients in their homes, reducing the need for hospital admissions and allowing healthcare systems to allocate resources more efficiently. Another innovative model is predictive healthcare, which utilizes AI and ML algorithms to analyze monitoring data and predict acute medical events before they occur, potentially saving lives and reducing healthcare costs.
The Role of Education and Training in the Adoption of Patient Monitoring Technologies
The successful implementation of patient monitoring technologies in Canada heavily relies on the education and training of healthcare professionals. As these technologies evolve, continuous professional development becomes essential to ensure that healthcare providers are proficient in using new devices and systems. Moreover, educating patients on how to use home monitoring devices and understand their health data is crucial for the success of RPM and other patient-centric models of care. Canadian educational institutions and healthcare organizations are increasingly incorporating digital health literacy into their curricula and training programs to meet this need.
Economic Impact of Advanced Patient Monitoring
The economic implications of adopting advanced patient monitoring technologies in Canada are multifaceted. On one hand, these technologies have the potential to significantly reduce healthcare costs by preventing hospital readmissions, managing chronic diseases more effectively, and optimizing the allocation of healthcare resources. On the other hand, the initial investment in technology and infrastructure, along with ongoing maintenance and training costs, poses financial challenges. However, the long-term savings and the potential for improved patient outcomes justify these investments, making patient monitoring a cost-effective solution for the Canadian healthcare system.
Ethical Considerations in Patient Monitoring
As patient monitoring technologies become more ingrained in healthcare, ethical considerations arise, particularly regarding patient autonomy, consent, and equity. Ensuring that patients have a clear understanding of how their data is used and maintaining their control over it is paramount. Furthermore, there is a need to address equity issues to prevent disparities in access to monitoring technologies, especially among vulnerable populations. Canadian healthcare policy makers and providers are tasked with navigating these ethical challenges, ensuring that the benefits of patient monitoring are realized ethically and equitably.
 Patient Monitoring in a Global Context
Patient Monitoring in a Global Context
While focusing on Canada, it’s important to place its advancements in patient monitoring within a global context. Canada is among the leaders in integrating patient monitoring technologies, but it also benefits from and contributes to global innovations and trends in this field. International collaborations, research exchanges, and policy dialogues play a crucial role in shaping the future of patient monitoring worldwide. By engaging in these global networks, Canada can both share its successes and learn from the experiences of other countries, fostering a collaborative approach to improving healthcare through technology.
Final Thoughts
The expansion of patient monitoring in Canada reflects a broader global shift towards more connected, efficient, and patient-centered healthcare. By embracing innovative care models, investing in education and training, understanding the economic landscape, navigating ethical considerations, and engaging in the global healthcare community, Canada is setting a standard for the future of patient monitoring. As technology continues to evolve, the Canadian healthcare system’s adaptability, commitment to equity, and focus on patient outcomes will be key drivers in realizing the full potential of patient monitoring for enhancing health and wellbeing across the nation and beyond.
Patient monitoring in Canada has come a long way, evolving from basic observational tools to complex digital systems. The integration of advanced technologies has significantly improved the ability to monitor and manage patient health, offering personalized and proactive care. However, challenges such as privacy concerns, the digital divide, and the need for standardization must be addressed to fully realize the potential of these technologies.
As Canada continues to navigate these challenges, the future of patient monitoring looks promising. With the ongoing integration of AI, ML, wearable technologies, and the expansion of telehealth, patient monitoring is set to become even more integral to healthcare. By focusing on technological advancement, addressing current challenges, and empowering patients, Canada can ensure that its healthcare system remains among the best in the world, offering high-quality, accessible, and efficient care to all its citizens.