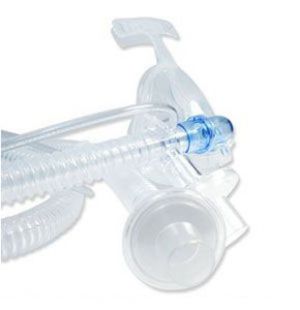
In the realm of anesthesiology, ensuring that a patient receives the right amount of anesthetic gases in a safe and efficient manner is of utmost importance. An integral part of this process is the anesthesia breathing circuit. This article dives into an overview of the anesthesia breathing circuit, its notable benefits, and addresses some commonly asked questions.
Anesthesia Breathing Circuit: An Overview
An anesthesia breathing circuit refers to the assembly of tubes and components that act as an intermediary between the anesthesia machine and the patient. It serves to deliver anesthetic gases and oxygen to the patient while also removing carbon dioxide. The two primary types are:
- Open Circuit: Used earlier in surgical history, this system released exhaled gases into the environment. Examples include the Schimmelbusch mask and Magill’s system.
- Closed or Semi-Closed Circuit: Nowadays, closed or semi-closed circuits are preferred. They recycle most of the exhaled gases after filtering and removing the carbon dioxide. Examples include the Circle system.
Benefits of Anesthesia Breathing Circuit:
- Conservation of Gas and Heat: Closed systems particularly conserve anesthetic gases and patient body heat, making procedures more efficient and comfortable for the patient.
- Safety: Modern circuits come equipped with fail-safes and monitors that reduce the risk of delivering a hypoxic mix (low oxygen content) to the patient.
- Flexibility: The design of these circuits allows for easy modification to cater to individual patient needs, be it adults, children, or infants.
- Humidification: The circuit can provide moisture to the gases the patient breathes, reducing the risk of a dry respiratory tract.
- CO2 Removal: Efficiently removes carbon dioxide from the patient’s exhaled gases, ensuring a fresh breath in the next cycle.
FAQs
Q: How often should the anesthesia breathing circuit be replaced?
A: The replacement or cleaning of the circuit depends on the hospital’s protocols and the specific type of circuit. Some circuits are disposable, while others are designed for multiple uses after thorough cleaning.
Q: Is there a risk of infection from the breathing circuit?
A: With proper cleaning, sterilization, or use of disposable components, the risk is minimal. However, it’s crucial to adhere to guidelines to prevent cross-contamination.
Q: How do anesthesia breathing circuits prevent the inhalation of CO2?
A: The circuits use a substance called soda lime or other CO2 absorbents to effectively remove carbon dioxide from the exhaled gases before the next inhalation.
Q: Can the same circuit be used for adults and children?
A: While the fundamental design remains consistent, circuits may need modifications or different sizes to cater effectively to adults, children, or infants.
In summation, the anesthesia breathing circuit is an indispensable tool in the anesthesiologist’s arsenal. It ensures efficient, safe, and comfortable delivery of anesthetic gases, adapting to the evolving needs of patients and surgical procedures. As technology advances, we can only anticipate further improvements in its design and functionality, solidifying its place in the medical field.